Comparisons
Comparison of Water Radiant Heating with Alternative Systems;
Advantages of Water Radiant Heating System Compared to Convection Heating Systems;
- There is no need for heating air at high temperatures (heat is transferred not by air, but by heat radiation from hot surfaces).
- It is not necessary to heat the entire volume (with heat radiation first the surfaces, people and machinery are heated, then the air).
- It is possible to separate the performance according to the zones (the zones where the high temperature is not needed can be closed without affecting the temperature in the areas where the system is operational).
- Water Radiant Heating does not require air circulation.
- It does not create dust and particle movement, it works silently.
- The air temperature under the ceiling is much lower than in air heating systems, which means much less heat loss (stratification effect).
- Since the surface temperatures (floor, wall, etc.) are high and do not create air movement, the feeling of comfort is much higher.
- Due to the radiation effect, the feeling of temperature is higher (the felt temperature is 2-3 °C higher than the ambient temperature), so the required comfort can be provided with lower set temperatures and thus energy savings can be achieved.
- By reducing the ambient set temperature by 1°C, it is possible to reduce fuel consumption by an average of 6%.
- With Water Radiant heating systems, it is possible to save up to 60% compared to air heating.
- Since there are no moving parts, service and maintenance costs are very low.
- The average lifetime of Water Radiant panels is 50 years.
- There is no risk of fire as it does not require electricity supply and combustion does not occur inside the space.
Advantages of Water Radiant Heating System Compared to Tube Radiant Heating Systems;
- With Water Radiant panels, up to 35% savings in operating costs can be achieved compared to tube radiant heaters. System efficiency is quite high compared to tube radiants. System efficiency in radiant heaters consists of the sum of combustion efficiency, thermal efficiency, radiant efficiency, control efficiency and design efficiency. While the combustion efficiency in Water Radiant panels can be optimized depending on the system used, in tube radiant heaters this value is constant and depends on the device burner. By using condensing systems, heat pumps and similar high efficiency systems, it is possible to save only about 12% in combustion efficiency with Water Radiant panels. While radiant efficiency can reach very serious values such as 79% in Water Radiant panels, this value is around 55% in standard tube radiants. In Water Radiant panels, water temperature and flow rate can be adjusted according to the need, and the control efficiency can reach values such as 99% thanks to the modulating heating systems. Most tube radiants are cascade, but even tube radiants with modulating burners are not as sensitive to varying heating needs as Water Radiant panels. The endless design possibilities of Water Radiant panels also make serious contributions to maximizing efficiency.
- Water Radiant panels provide a more homogeneous heating compared to tube radiants.
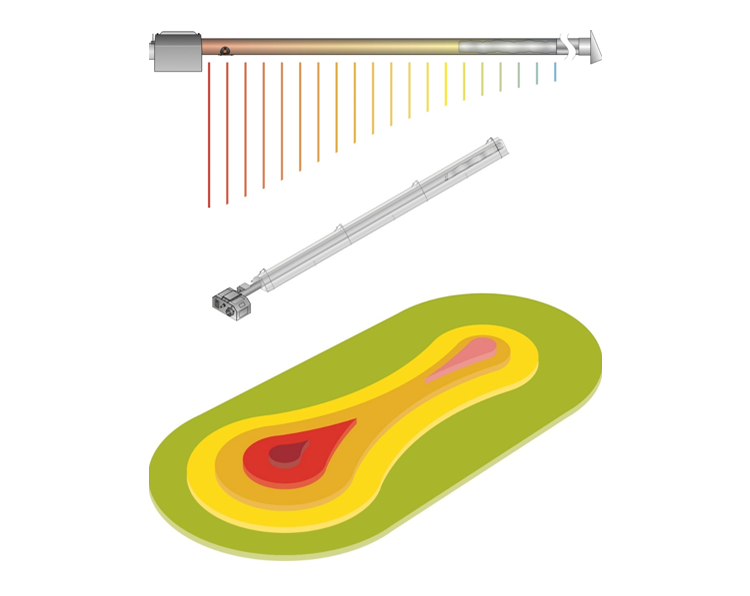
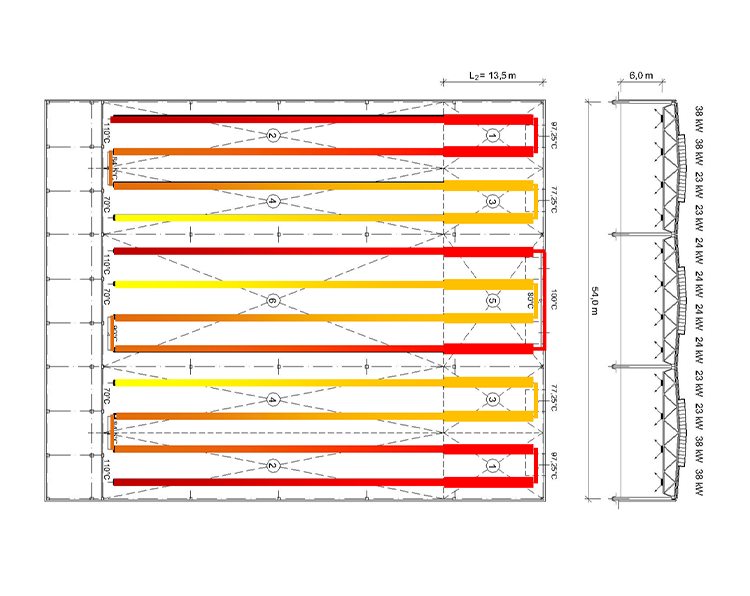
The heat map of the area affected by a straight tube radiant is shown in the tube radiant graph, and an example Water Radiant application is shown in the Water Radiant graph. In tube radiants, the average temperature in the region where the combustion takes place is 650 C, and the average temperature in the area where the waste gas is discharged is approximately 150 C. Due to the 500 C degree difference, an inhomogeneous heat distribution occurs in the impact area and this creates discomfort. In Water Radiant panels, on the other hand, the round-trip temperature difference can be selected between 5 C degrees and 40 C degrees depending on the design. In addition, it is possible to provide a completely homogeneous heating by overlaping the influence areas of the flow lines (hottest line) and return lines (coldest line) in Water Radiant panels.
- Thanks to their large surface areas and relatively low surface temperatures, Water Radiant panels do not create the discomfort caused by the high surface temperatures of tube radiants and provide much more comfortable heating.
- In order to remove the waste gases that will be released as a result of combustion in tube radiants, chimney application is required for each device. In the use of Water Radiant panel, there is no need for any chimney application in the space. No action is carried out on the roof or walls of the structure, the structure has a much more stylish appearance both from the inside and from the outside. The use of water radiant panels provides very serious advantages in cases where chimney application is not possible or difficult.
- In tube radiant applications, a natural gas pipeline must be drawn at each device entrance and safety equipment must be installed. This requires serious piping and labor. In the In the water radiant heating system, hot and cold water pipes to be drawn along parallel radiant lines are sufficient for the operation of the system.
- Water Radiant heating is completely silent, while in tube radiant heating, there is a noise due to the burner and fan.
- There is no natural gas or electricity connection in Water Radiant panels. Therefore, there is no risk of fire or leakage originating from the Water Radiant panel. In tube radiants, there is a risk of leakage and fire since both combustion takes place inside the device and electricity supply is required for the burner and fan. In addition, since the surface temperatures are very high in tube radiant heaters, it is necessary to keep a certain distance between the equipment and the tube radiants and insulate them in order not to damage the equipment (cables, etc.) close to the heater surface and not cause a fire.
- Since there are no moving parts in Water Radiant panels, there is no risk of failure, and maintenance and service costs are very low. The warranty period of Water Radiant panels is 10 years, and the average lifetime is 50 years. Tube radiants, on the other hand, have equipment that requires maintenance and can be a source of failure, such as a burner. Therefore, the risk of failure, maintenance and service costs are high. Although the warranty period varies from manufacturer to manufacturer, the maximum service life is around 10-15 years.
- It is not possible to use any fuel other than natural gas or LPG for tube radiant heaters. However, since Water Radiant panels work with hot water, it is possible for the panels to work with any heat source that can produce hot water. Therefore, Water Radiant panels can be used with fuels such as natural gas, LPG, biogas, pellets, sawdust, wood, coal, electricity (heat pump or electric boiler-combi) as well as steam, geothermal energy or any available waste heat obtained from the facility by transferring the heat to water through heat exchangers.
- In facilities that release unused heat or wastes that can be an energy source when burned (such as sawdust) as a result of the process, facility heating can be carried out at very low costs and even at zero cost by using Water Radiant panels. It is not possible to use these wastes in tube radiant heaters.
- Tube radiant heaters have a lower surface area compared to Water Radiant heaters, so their area of influence is lower. Therefore, when it is desired to heat a certain area, Water Radiant panels can be designed to be exactly suitable for the required capacity, while in tube radiant heaters, the capacity may need to be selected far above the need in order to provide the desired area of influence. This causes the installed power to increase. Gas companies collect security deposit from facilities that request natural gas subscription and are outside the organized industrial zones. This security fee is calculated over the maximum natural gas cost that can be consumed in the facility for two months. It is charged at the time of subscription and refunded when the subscription is terminated. When calculating the maximum amount of natural gas that can be consumed in the facilities, the total installed power of gas burning devices is taken as a basis rather than the actual consumption. Therefore, the higher the installed power, the higher the assurance fee. Considering the continuity of the facility, the security deposit can also be considered as a cost item. The low installed power in Water Radiant panels creates a serious advantage over tube radiant heaters in this respect.
- Water Radiant panels can be used for cooling as well as heating if needed. Tube radiants do not have such an option.
Advantages of Water Radiant Heating System Compared to Ceramic Radiant Heating Systems;
- With Water Radiant panels, up to 35% savings can be achieved in operating costs compared to ceramic radiant heaters. System efficiency is quite high compared to ceramic radiants. System efficiency in radiant heaters; Combustion efficiency is the sum of thermal efficiency, radiant efficiency, control efficiency and design efficiency. While the combustion efficiency in Water Radiant panels can be optimized depending on the system used, in ceramic radiant heaters this value is constant and depends on the device. By using condensing systems, heat pumps and similar high efficiency systems, it is possible to save only about 18% in combustion efficiency with Water Radiant panels. While radiant efficiency can reach very serious values such as 79% in Water Radiant panels, this value is around 60% in standard ceramic radiants. In Water Radiant panels, water temperature and flow rate can be adjusted according to the need, and the control efficiency can reach values such as 99% thanks to the modulating heating systems. Ceramic radiants, on the other hand, are available in stepped and modulated models, but even modulated ceramic radiants cannot respond to variable heating needs as precisely as Water Radiant panels. The endless design possibilities of Water Radiant panels also make serious contributions to maximizing efficiency.
- Water Radiant panels provide a more homogeneous heating compared to ceramic radiants.
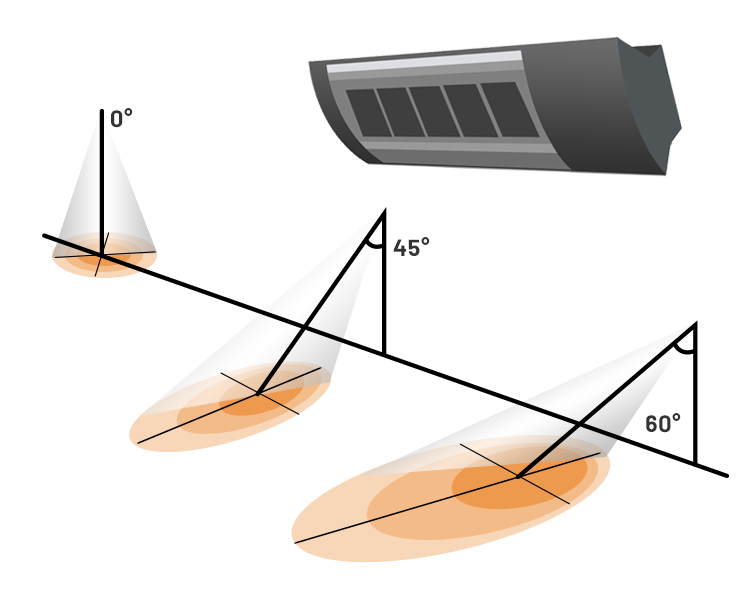
Ceramic radiant heaters are devices designed mainly for spot heating. Therefore, although the area they scan with radiation varies according to the hanging shape and angle, it is generally quite low when compared to Water Radiant panels. Due to the high surface temperatures of around 900 °C, the temperature felt in the irradiated area is much higher than in the unscanned area. Water Radiant panels, on the other hand, heat all surfaces homogeneously, thanks to their wider surface and impact areas. Since the surface area and therefore the impact area of the ceramic radiants are small, it is very difficult to scan all the surfaces in the space.
- Thanks to their large surface areas and relatively low surface temperatures, Water Radiant panels do not create the discomfort caused by high surface temperatures of ceramic radiants and provide much more comfortable heating. In Water Radiant panels, there is no cold zone as the entire space is heated.
- There is no chimney application in ceramic radiant heaters as in tube radiant heaters. As a result of combustion, waste gases are released to the environment. In order to remove these waste gases from the environment, a minimum of 10 m³/h ventilation should be made for each kW of ceramic radiants. This value is well above the standard ventilation requirement of the space. The need for additional ventilation will cause both electricity and natural gas consumption since it will cause extra heat losses.
- In ceramic radiant applications, a natural gas pipeline must be drawn at each device entrance and safety equipment must be installed. This requires serious piping and labor. In the Water Radiant heating system, hot and cold water pipes to be drawn along parallel radiant lines are sufficient for the system to work.
- There is no natural gas or electricity connection in Water Radiant panels. Therefore, there is no risk of fire or leakage originating from the Water Radiant panel. In ceramic radiants, on the other hand, there is a risk of leakage and fire as they are open flame devices. In addition, since the surface temperatures of ceramic radiant heaters are very high, it is very risky to use them in places where there are potentially flammable materials (textiles, etc.) or flammable solutions.
- Since there are no moving parts in Water Radiant panels, there is no risk of failure, and maintenance and service costs are very low. The warranty period of Water Radiant panels is 10 years, and the average lifetime is 50 years. In ceramic radiants, on the other hand, it is necessary to clean the ceramic plate surfaces regularly. Since they are used in high quantities, their maintenance and service costs are high. Although the warranty period varies from manufacturer to manufacturer, the maximum service life is around 10-15 years.
- It is not possible to use any fuel other than natural gas or LPG for ceramic radiant heaters. However, since Water Radiant panels work with hot water, it is possible for the panels to work with any heat source that can produce hot water. Therefore, Water Radiant panels can be used with fuels such as natural gas, LPG, biogas, pellets, sawdust, wood, coal, electricity (heat pump or electric boiler-combi) as well as steam, geothermal energy or any available waste heat obtained from the facility by transferring the heat to water through heat exchangers.
- In facilities that release unused heat or wastes that can be an energy source when burned (such as sawdust) as a result of the process, facility heating can be carried out at very low costs and even at zero cost by using Water Radiant panels. It is not possible to use these wastes in ceramic radiant heaters.
- Since ceramic radiant heaters have a very low surface area compared to Water Radiant heaters, their area of influence is much lower. Therefore, when it is desired to heat a certain area, Water Radiant panels can be designed to be exactly suitable for the required capacity, while in ceramic radiant heaters, the capacity may need to be selected far above the need in order to provide the desired area of influence. This causes the installed power to increase. Gas companies collect security deposit from facilities that request natural gas subscription and are outside the organized industrial zones. This security fee is calculated over the maximum natural gas cost that can be consumed in the facility for two months, is collected during subscription and returned when the subscription is terminated. When calculating the maximum amount of natural gas that can be consumed in the facilities, the total installed power of gas burning devices is taken as a basis rather than the actual consumption. Therefore, the higher the installed power, the higher the assurance fee. Considering the continuity of the facility, the security deposit can also be considered as a cost item. The low installed power in Water Radiant panels creates a serious advantage over ceramic radiant heaters in this respect.
- Water Radiant panels can be used for cooling (cooling) as well as heating if needed. Ceramic radiants do not have such an option.