Water Radiant Heating
What is Radiant Heating?
Radiant heating is the transfer of heat from a hot object in the same environment to another object with a lower temperature by means of electromagnetic wave energy. This is due to the radiation effect, a phenomenon that allows heat to be transferred from an object to the surrounding structures.
Radiation is a natural mechanism by which a cold surface absorbs heat contained or generated by a surface with a higher temperature than itself. Absorbed heat is the heat transferred through thermal radiation. In radiation, the air in the environment does not prevent heat transfer, first the objects in the environment and then the whole ambient air warms up.
The heating of the Earth by the sun is also based on this principle.
What is Radiation?
Radiation is one of three ways in which heat is transferred. Thermal radiation, on the other hand, is electromagnetic energy in the field of infrared rays. Heat transfer by radiance takes place by means of thermal radiation. Unlike conduction and convection, heat by radiation (thermal radiation) have the advantage of spreading in a vacuum (airless environment), and this energy is absorbed by the surface of solid objects instead of air. This means that there is no energy transfer to the ambient air. Infrared waves travel easily through air and space and only generate heat when they strike an object such as the surface of the ground or the wall of a house. When the thermal radiation emitted by the infrared ray system hits an object (walls, floors, interior objects), the affected molecules begin to oscillate under the action of the rays. The energy continues to be absorbed by the molecules of the object until the oscillation frequency reaches the frequency of the thermal radiation. After this point, thermal radiation begins to be reflected. Humans perceive the effect as a temperature state caused by the increased energy of their molecules. Thermal comfort is a combination of air temperature and surface temperature.
Therefore, the first feeling that occurs when entering an environment heated by radiation is comfort. As a practical example, when moving from a shaded area to a sunny area, a higher temperature is felt, although the air temperature remains the same. This is due to the fact that the feeling of temperature is caused not only by the temperature of the air, but also by a combination of air temperature and surface temperature. As the surface temperature rises due to direct exposure to sunlight, the perceived temperature also increases.
HEAT TRANSFER BY RADIATION: The maximum amount of radiation that a surface can emit depending on the absolute temperature Ts is determined by Stefan Boltzman’s law. As can be understood from the formula, heat transfer by radiation depends on emissivity, surface area and the fourth power of surface temperature. The formula expresses the maximum amount of radiation a surface can emit. The amount of heat that can be transferred by radiation between two surfaces is obtained by arranging Ts as the temperature difference between the surfaces in the same formula. Therefore, the greater the emissivity value of the surface, the temperature difference and the surface area, the higher the amount of energy that can be transferred by radiation.
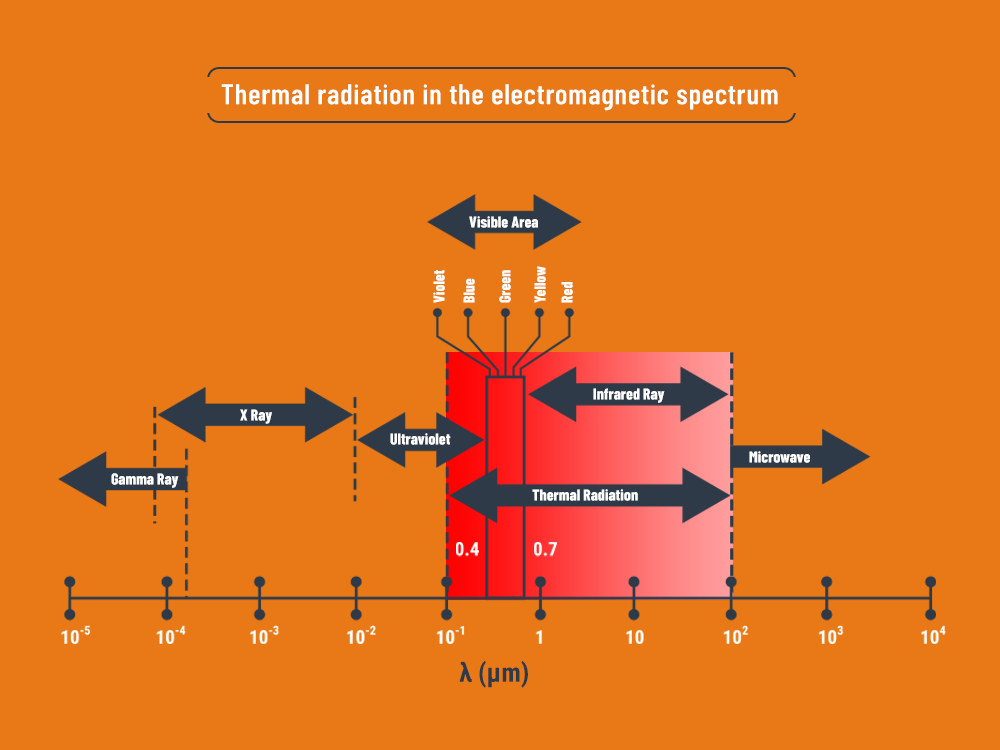
IR RAYS: Infrared radiation is also called thermal radiation because our body perceives it as heat. Infrared radiation is a natural radiation that we encounter every day in many different forms. While the sun emits infrared radiation and warms the earth, hot objects also emit infrared radiation.
The term “infrared,” meaning lower than red, indicates that its frequency is just below the red color of visible light. In practice, any surface with a temperature above absolute zero (0° K = -273.15° C) emits radiation in this band. The higher the surface temperature, the higher the heat dissipation and therefore the infrared radiation.
ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM: The wavelength range in which thermal radiation is effective is specified in the electromagnetic spectrum. For Water Radiant heating systems, the effective range of radiation is limited to the wavelength range of infrared rays. Therefore, it does not have harmful effects on human health such as gamma rays, x rays, ultraviolet rays.
Water Radiant Heating;
Water Radiant Heating Systems have been actively used in the world since the 1950s, but in recent years, parallel to the increasing importance given to comfort and energy efficiency, the interest and demand for Water Radiant heating systems has increased significantly. Water Radiant panels basically consist of precision steel pipes, radiant panels (aluminum or coated sheet), insulation and assembly equipment. To explain in the simplest way, the pipes in which hot water is circulated heat the surface of the radiant panel. Heated special coated panels transfer their heat to living things and objects in the environment that needs to be heated by means of radiation (infrared rays). The energy transferred by the Water Radiant panels primarily heats these living things and objects, and then the ambient air. The hot water production required to supply the water circulating in the pipes can be provided by boilers using any kind of fuel, heat pumps or waste heat sources. The hot water prepared in the heat generator is transmitted through pipes to the radiant panels mounted on the ceiling of the room to be heated. The hot water circulated in the radiant panel returns to the heat source after transferring its heat to the panels.

Water Radiant panels are modular structures. Required panel surface areas can be obtained by combining the desired number of modules of certain sizes. In this way, the heat need of any space can be met fully and accurately. The interconnected Water Radiant panels not only create the required heating surface area, but also serve as a distribution pipeline. In this way, piping costs and labor in the space are also saved. Heating of an environment with radiant panels arranged evenly on the ceiling ensures that the floor temperature is always several degrees higher than the room indoor air temperature. This creates a more natural and comfortable warming feeling. With Hot Water Radiant panels, it is possible to save more than 40% energy compared to other systems in the heating of industrial facilities, warehouse areas, sports halls, train maintenance stations, aircraft hangars, amphitheaters, animal farms, greenhouses and similar high-ceilinged structures. Water Radiant panels have many important features, especially when considering the heating of buildings with high ceilings and/or high fire risk.



COMFORTABLE!
- Provides homogeneous temperature distribution
- Does not create any airflow
- Works silently
- Creates extra comfort thanks to high radiation effect
- Provides optimum comfort thanks to the high floor temperatures it creates.
ECONOMIC!
- No maintenance and service costs
- Can also work with renewable and waste energy sources
- Provides High Energy Efficiency (radiant efficiency up to 79%)
- No obligation to use natural gas (coal, sawdust, pellets, and similar fuels can be used)
- Panels in unused areas can be closed with the help of motorized valves
PRACTICAL!
- Easy and fast to install
- Admission time is very low
- Adaptable to use at any ceiling height (2,5 meters – 40 meters)
- No need for chimney or additional ventilation in the space
- The need for piping is minimal
HEALTHY!
- Ambient air is clean as no combustion gas is released into the ambient air
- Since it does not create any air flow, there is no dust and particle circulation.
SAFE!
- No risk of fire
- No risk of flashing or explosion
- No risk of waste gas or natural gas leakage in the area
ECO FRIENDLY!
- Thanks to high efficiency, it minimizes the Nox and CO2 emission of the heating system
- Can be used with renewable energy sources and waste heat
COMPACT, ADAPTABLE AND STYLISH!
- Provides the possibility of mounting in height, width and length according to the needs
- Space-saving as it is mounted on the ceiling
- Both heating and cooling can be provided with the same panels.
- Gives an aesthetic appearance to the area with its simple and elegant appearance.
- Creates integrity in the area with the possibility of being produced in the desired RAL color.
AREA of IMPACT and DESIGN OPTIMIZATION;
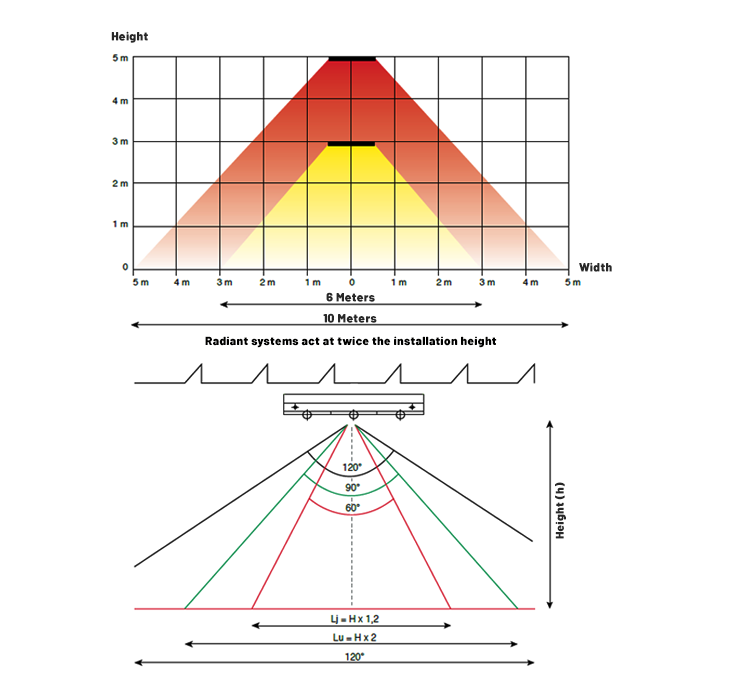
The total capacity of Water Radiant panels is determined according to the heat loss. However, in order to provide homogeneous and comfortable heating, the placement of the panels is also very important in addition to the capacity. Water Radiant panels affect an area approximately twice the hanging height.
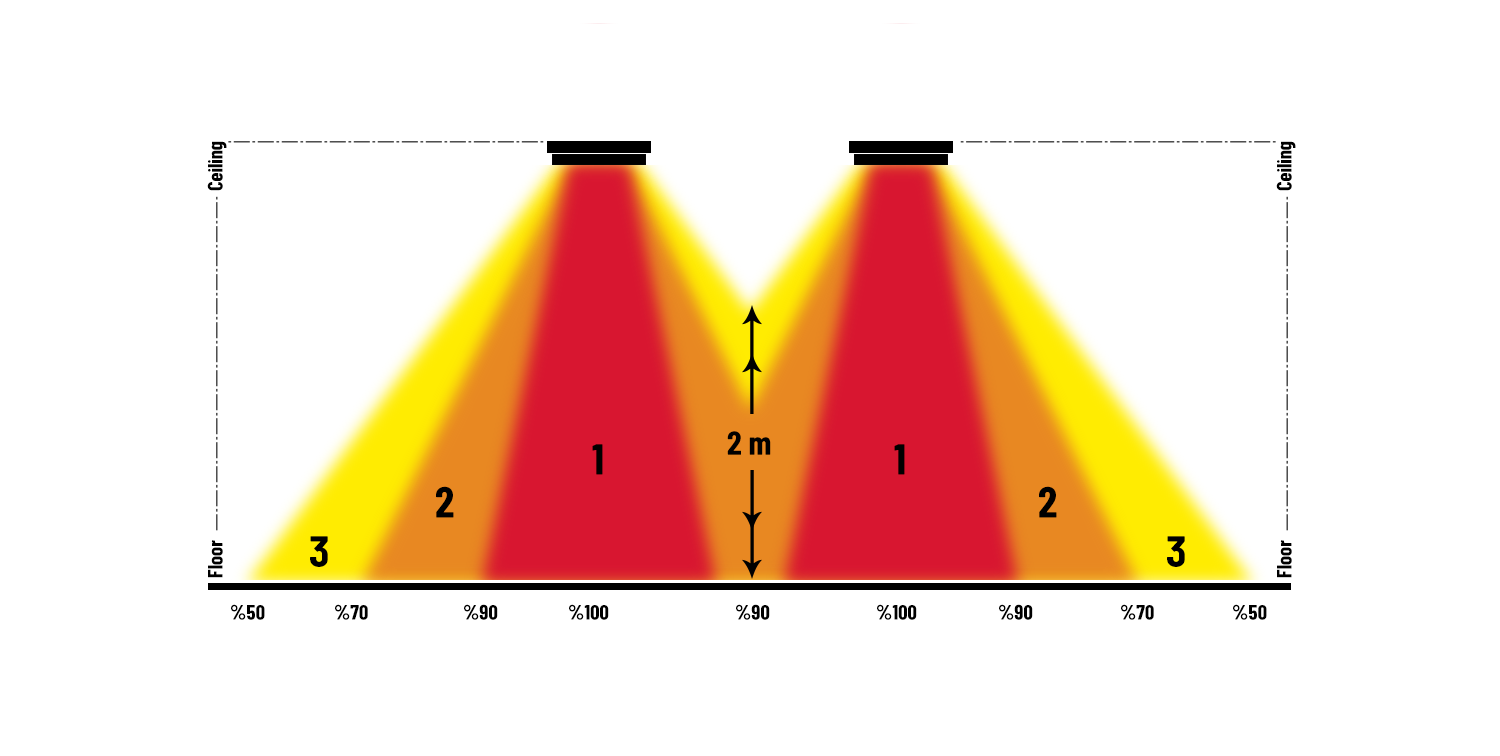
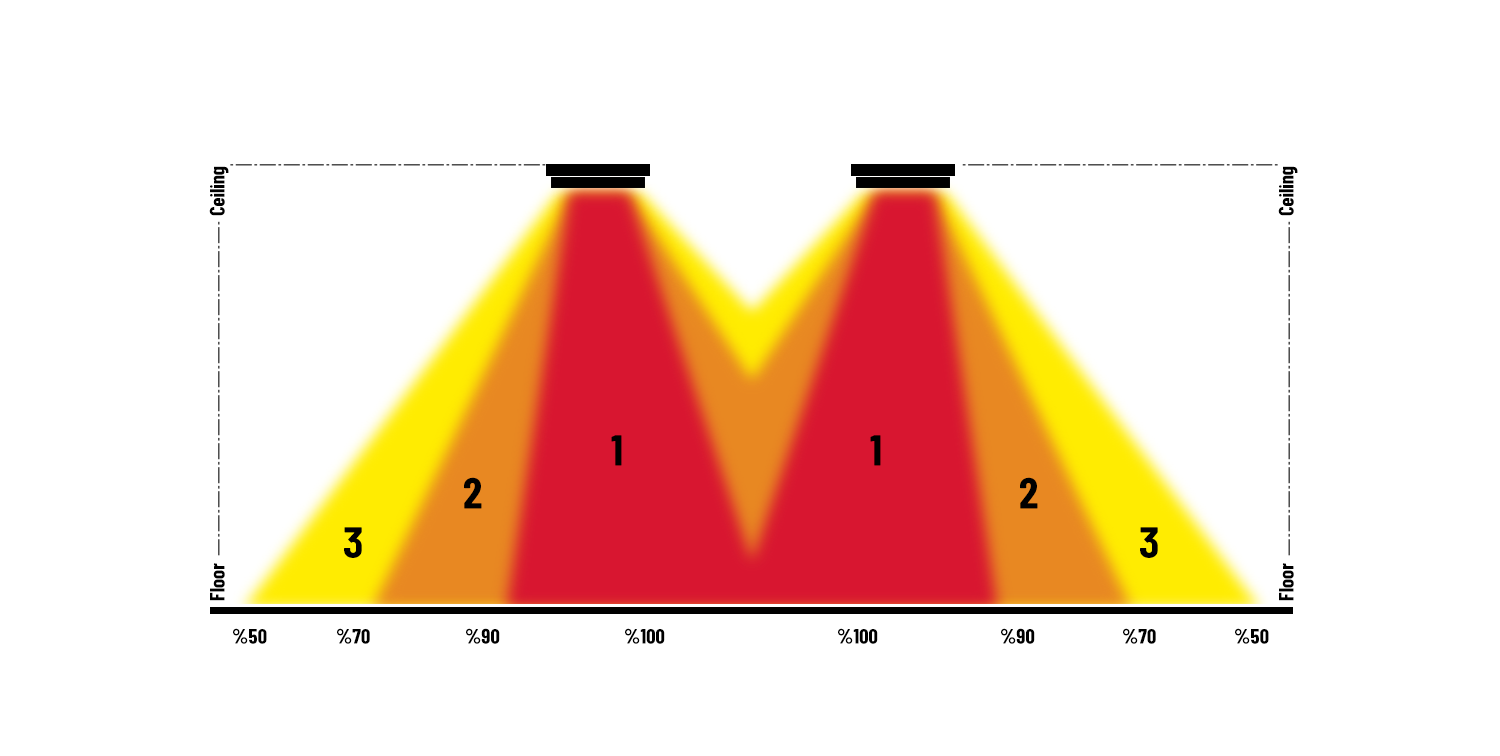
If the spheres of influence are divided into Zone One, dense spheres of influence, Zone Two, standard spheres of influence and Zone Three, low spheres of influence: